How Does Dietary Fiber Affect Blood Sugar
Unfortunately dietary fiber represents a heterogenous category and there is still much to understand as to which foods should be preferred to maximize the metabolic effects of fiber.
How does dietary fiber affect blood sugar. You get carbs. The amount of daily dietary fiber intake considered to be helpful in managing blood sugar levels is at least 25 and 38 grams per day in women and men respectively. When you watch your diet because you have diabetes you ll want to pay special attention to carbohydrates because they can affect your blood sugar level faster than protein or fat.
Research has consistently shown that for people with type 2 diabetes eating more fiber can help improve blood glucose control. If diet and exercise aren t enough to manage blood sugar those with type 2 diabetes may be prescribed medications to help keep blood sugar levels within target ranges. Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that your body can t digest so you should subtract the grams of fiber from the total carbohydrate.
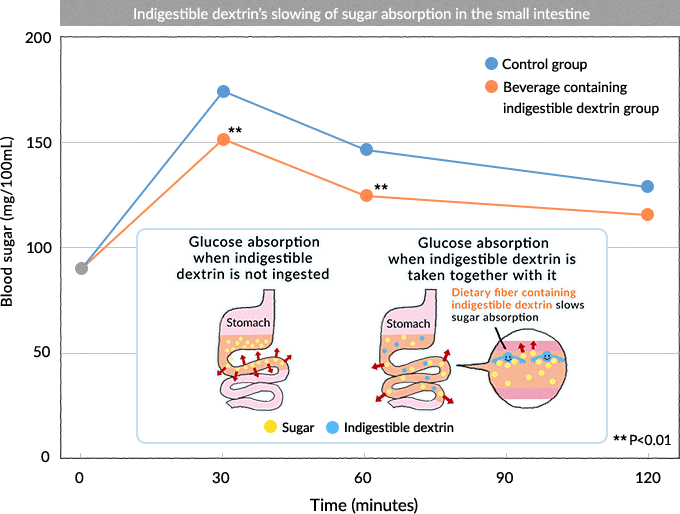
Reducing blood sugar spikes helps promote more balanced blood sugar levels throughout the day. Fiber slows down the rate you process a meal at preventing postmeal spikes in blood sugar by slowing the absorption of simpler carbohydrates. If you have type 2 diabetes you should be including high fiber foods in your diet is a healthy way to control high blood sugar.
On nutrition facts food labels the grams of dietary fiber are already included in the total carbohydrate count. Fiber is subtracted from total carbohydrates because it doesn t raise blood sugar since it can t be digested. Helps control blood sugar levels.
A healthy diet that includes insoluble fiber may also reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. However these recommendations have been questioned on the basis of growing evidence that in both insulin dependent and non insulin dependent diabetic patients a high carbohydrate diet does not offer. There are indications that only water soluble fiber is active on plasma glucose and lipoprotein metabolism in humans.
Fiber does not affect your blood sugar levels. In people with diabetes fiber particularly soluble fiber can slow the absorption of sugar and help improve blood sugar levels. Aids in achieving healthy weight.


















