Dietary Fiber And Crude Fiber

The recommended intake of dietary fiber is 14 g per 1 000 calories consumed.
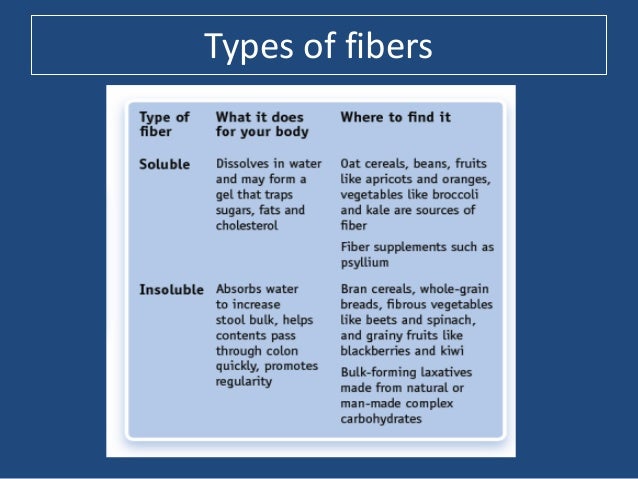
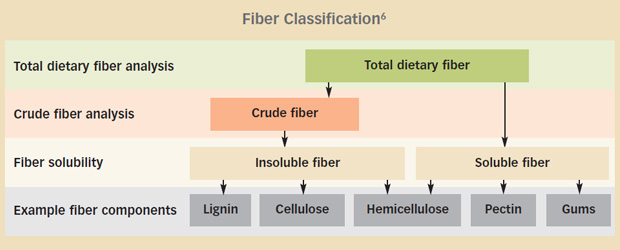
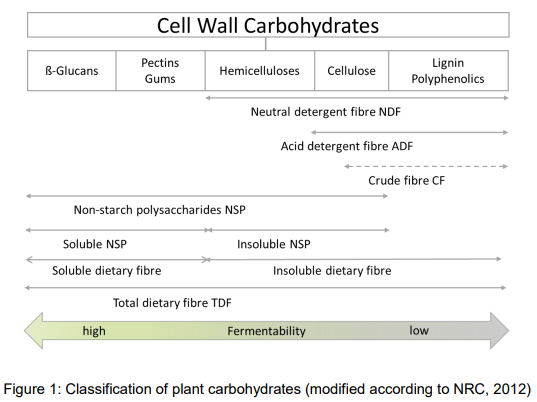
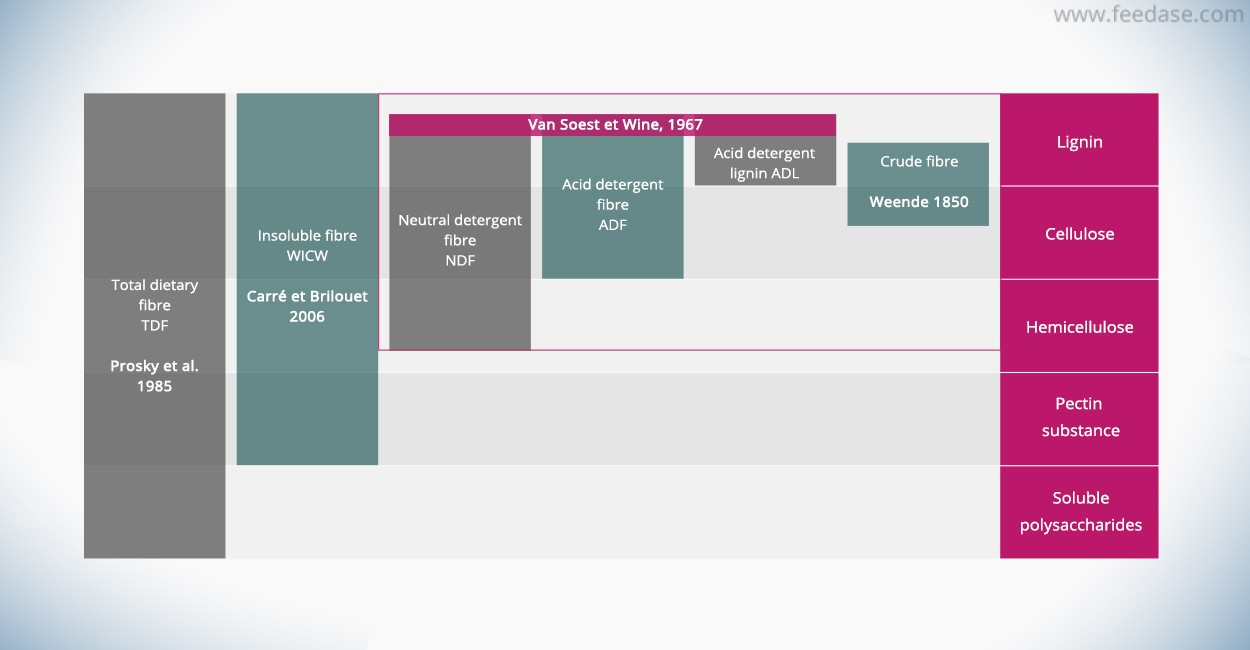
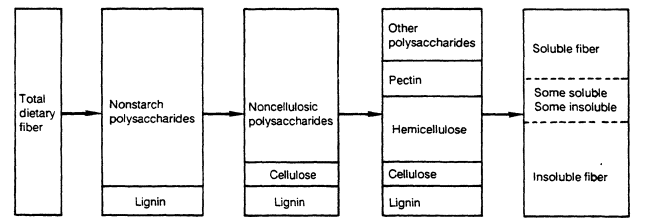
Dietary fiber and crude fiber. There is crude fiber which is what laboratory testing comes up with when testing a food item. Dietary fiber is found in plants typically eaten whole raw or cooked although fiber can be added to make dietary supplements and fiber rich processed foods grain bran products have the highest fiber contents such as crude corn bran 79 g per 100 g and crude wheat bran 43 g per 100 g which are ingredients for manufactured foods. Dietary fiber is a complex mixture of different components.
Finally there is functional fiber that is a term used to refer to not just dietary fibers but also other fibers made artificially in labs. That translates into a need for 25 to 35 g of fiber per day in a typical diet. It is the sum of both soluble and non soluble fiber groups.
Ammonia nh 3 emission is a major concern for the poultry industry. From then on the term crude fiber was replaced by df gradually. Artificial fiber is added to packed foods to enhance their nutritional values by manufacturers.
Effects of dietary fiber and reduced crude protein on ammonia emission from laying hen manure. Over mature products have increased levels of crude fiber. Crude fiber on the other hand is a term used to describe the fibrous food residue that is left over after it has been dissolved in the laboratory with certain harsh chemical solvents such as sulfuric acid and sodium.
Today s accepted term for fiber is dietary fiber but this term has only been in use since late 1970s. Crude fiber is part of insoluble fiber found in the edible portion of the plant cell wall. Crude fiber is also useful in the chemical determination of succulence of fresh vegetables and fruits.
Roberts sa 1 xin h kerr bj russell jr bregendahl k. Key difference dietary fiber vs crude fiber dietary fiber is an indigestible portion of food derived from plants. 1 department of animal science iowa state university ames ia 50011 usa.