Structure Of Dietary Fiber

Relationship between structure and function of dietary fibre.
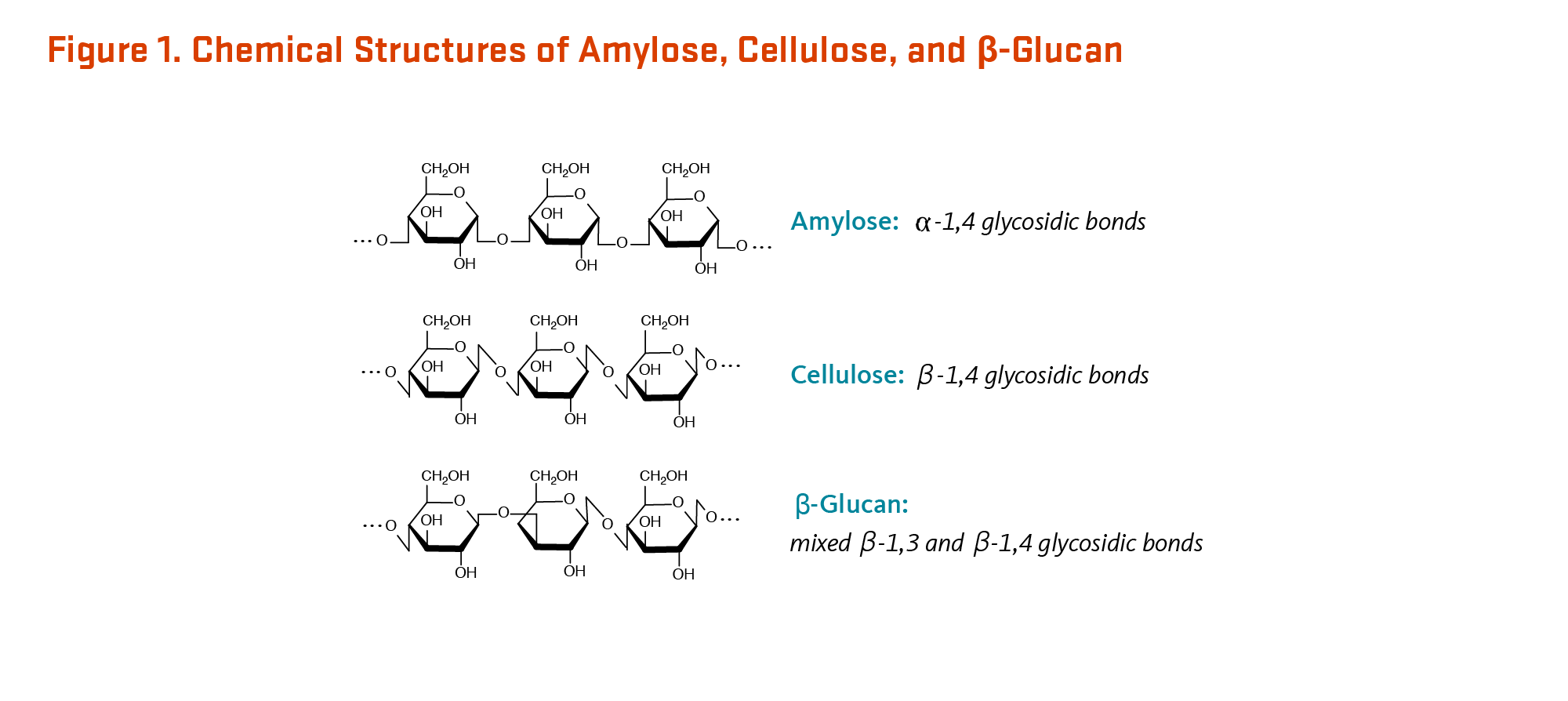
Structure of dietary fiber. Dietary fiber includes cellulose hemicelluloses pectin and lignin. It contains a mixture of chemically complex polysaccharides. The term dietary fiber can be considered a black box since the structure of fiber can vary in monomeric composition chain length type of binding branching and side chains.
Dietary fiber is a ubiquitous component of plant foods including materials of diverse chemical and morphological structure. In recent years diabetes obesity and other health issues of human beings increased significantly due to low dietary fiber intake. The epidemiologic data on the benefits of dietary fiber lack the control necessary to determine whether it is the fiber or another aspect of a high fiber diet that delivers a benefit.
It has two main components. Dietary fibre includes non starch polysaccharides and lignin that are not digested or absorbed in the human small intestine. Another way to get fiber is through natural supplements such as psyllium which is made from the seed of a shrub like herb.
Soluble fiber which dissolves in water is generally fermented in the colon into gases and physiologically active by products such as short chain fatty acids produced in the colon by gut bacteria. The physical and chemical structure of dietary fiber is a key factor in determining the rate of fermentation the distribution of scfas and the growth of different bacterial populations wang wichienchot he fu huang 2019. Dietary fiber has gained a lot of public attention.
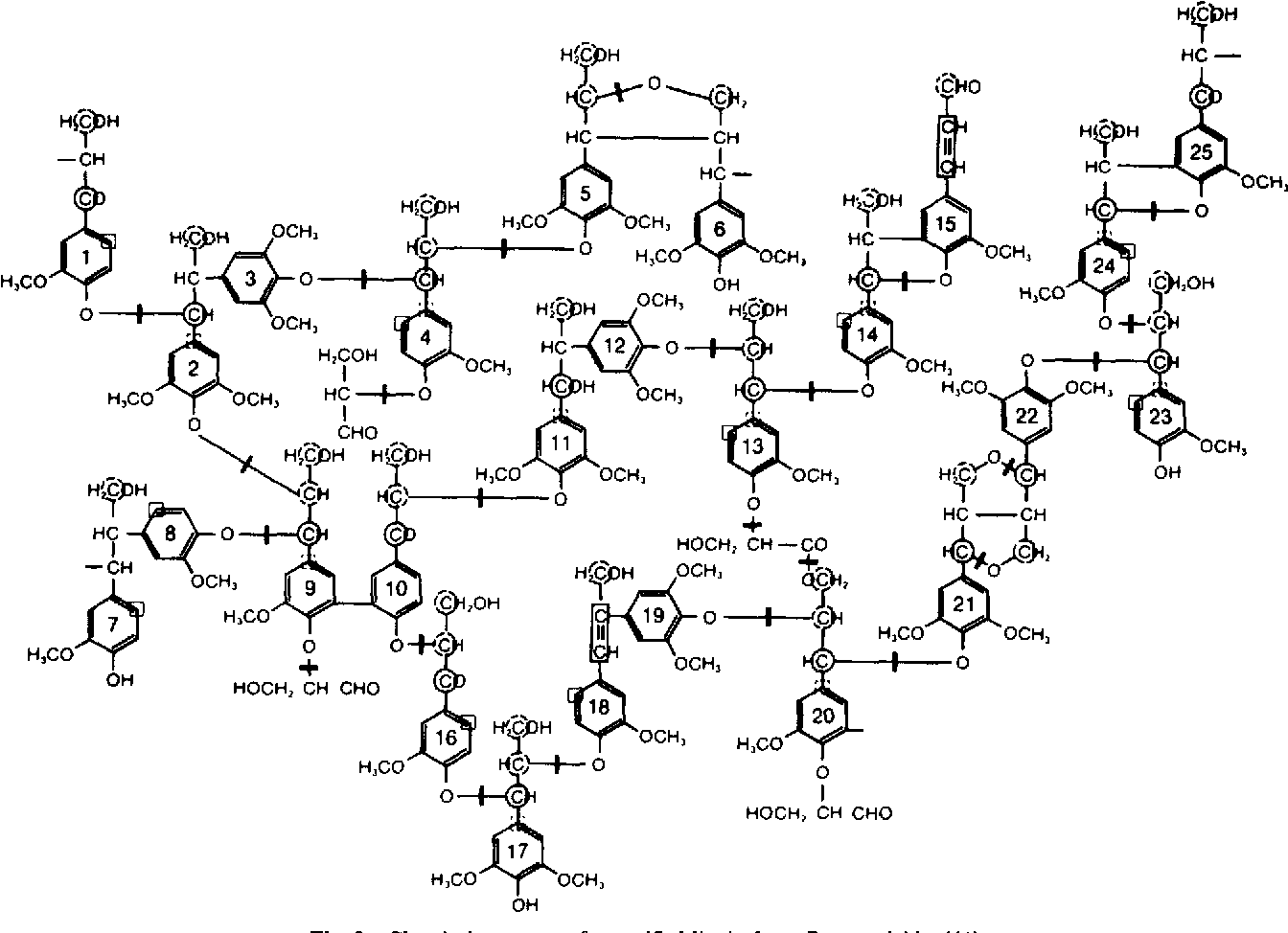
Consists of nondigestible carbohydrates and lignin that are intrinsic and intact in plants. In contrast to dietary fiber which is intrinsic and intact in foods isolated fiber e g fiber supplements can be assessed for a direct effect on specific. Lignin is a highly cross linked complex polymer of phenylpropane units.
The plant cell wall is the main source of dietary fibre and its structure is reviewed. For example arabinoxylans can vary in their arabinose. A comparative study of the effects of three galactomannans on cholesterol metabolism in the rat volume 68 issue 1 a.