Dietary Vitamin K Intake And Anticoagulation In Elderly Patients
Patients were considered with a stable anticoagulation when their inr coefficient of variation was less than 10.
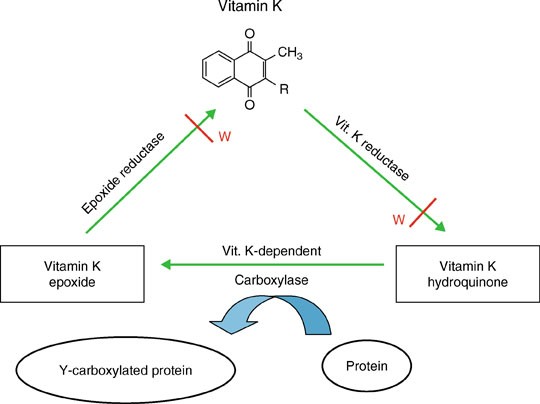
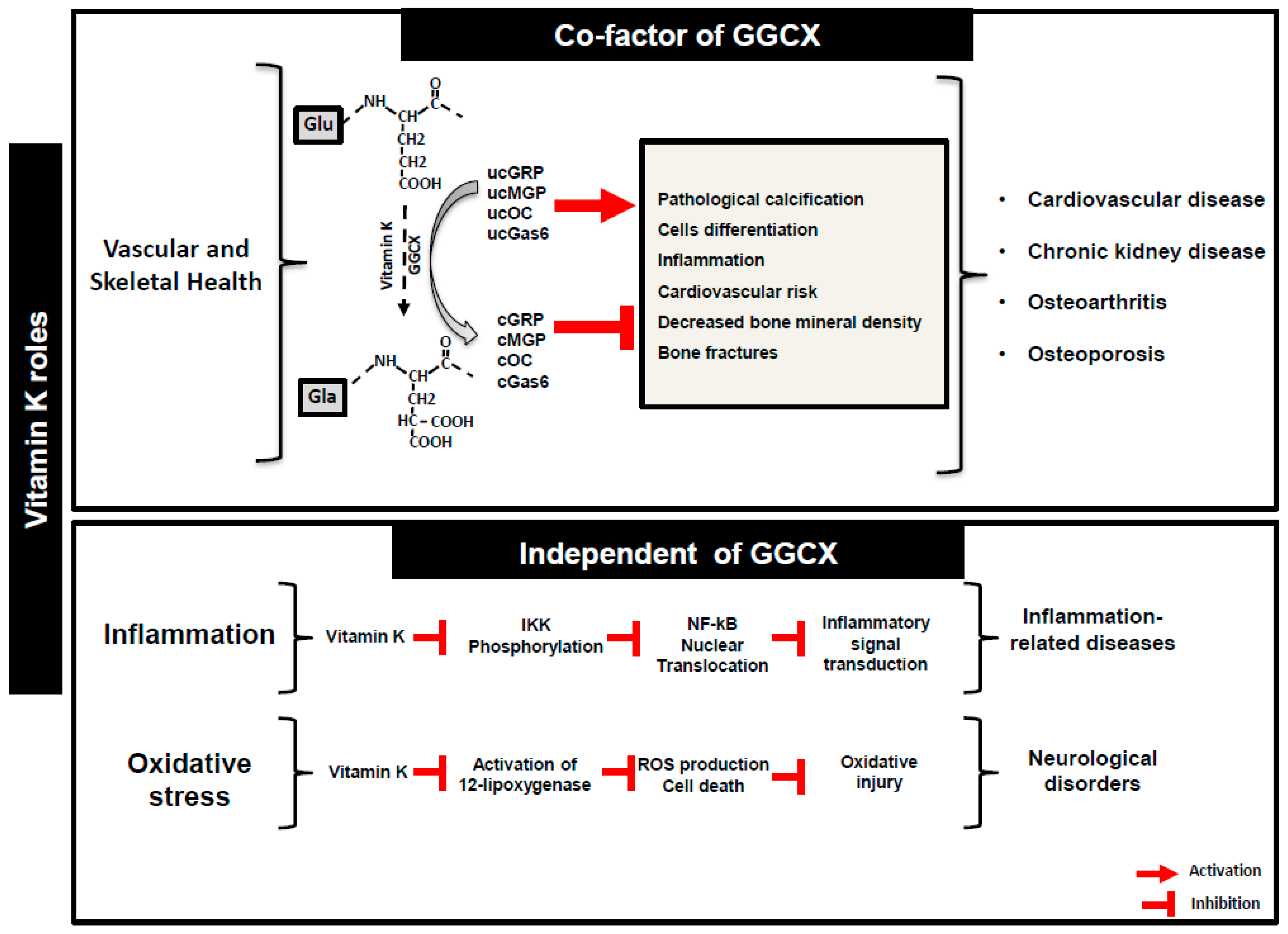
Dietary vitamin k intake and anticoagulation in elderly patients. Oral anticoagulants competitively inhibit enzymes that participate in vitamin k metabolism. 23 patients 17 were achieved stable anticoagulation. The purpose of this review is to evaluate the potential interaction of dietary vitamin k and coagulation stability particularly in the elderly patient.
Ation stability particularly in the elderly patient. In a randomized crossover study brief periods of changes on vitamin k. Dietary vitamin k intake and anticoagulation in elderly patients.
Purpose of reviewvitamin k is an essential co factor for the synthesis of several coagulation factors. Stable and unstable patients had no significant differences in baseline characteristics. We studied 132 patients on chronic oa 57 13 years.
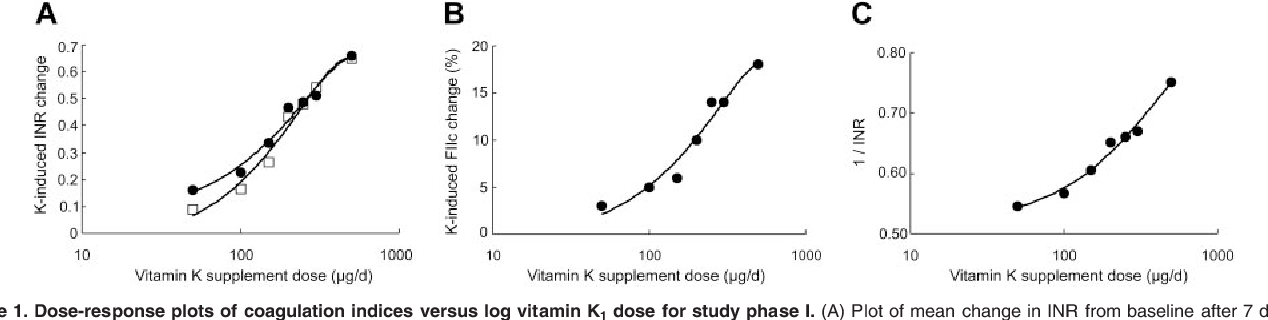
Median dietary intake of vitamin k1 ranged from 76 to 217 μg day among studies and an effect on coagulation may be detected only for high amount of vitamin intake 150 μg day. Request pdf dietary vitamin k intake and anticoagulation in elderly patients vitamin k is an essential co factor for the synthesis of several coagulation factors. Concomitant supplementation of vitamin k perhaps through reducing the relative day to day variability in dietary vitamin k intake can significantly improve anticoagulation control in patients.
The purpose of this review is to evaluate the potential interaction of dietary vitamin k and coagulation stability particularly in the elderly patient. Recent findings recent prospective evidences suggest that dietary vitamin k plays an essential role in anticoagulation stability. Inr and vitamin k intake were prospectively collected at baseline 15 30 60 and 90 days after randomization.
Oral anticoagulants competitively inhibit enzymes that participate in vitamin k metabolism. Vitamin k is an essential co factor for the synthesis of several coagulation factors. The purpose of this review is to evaluate the potential interaction of dietary vitamin k and coagulation stability particularly in the elderly patient.