Dietary Fibre Meaning In Science

It has become clear that an internationally acceptable definition of dietary fiber must link specific physiological effects of dietary fiber with workable analytical methods that are.
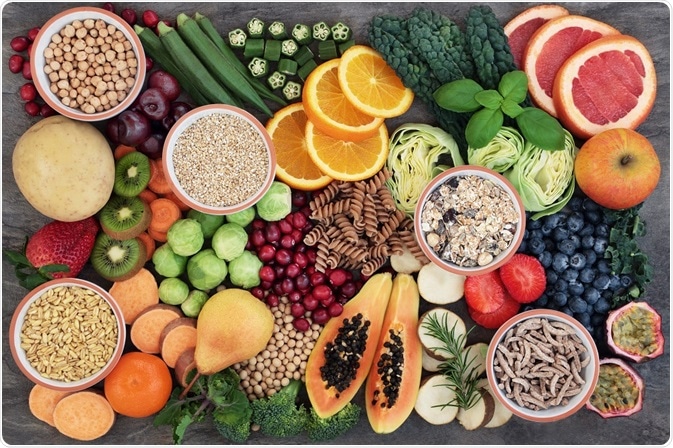
Dietary fibre meaning in science. Large intestine digestion of dietary fibre. N fibrous substances in fruits and vegetables such as the structural polymers of cell walls consumption of which aids digestion and is believed to help. The intestinal bacteria and the cells lining the large intestine can then use these smaller molecules as an energy source.
It is a type of carbohydrate but unlike other carbs it cannot be broken down into digestible sugar molecules. Soluble fiber which dissolves in water is generally fermented in the colon into gases and physiologically active by products such as short chain fatty acids produced in the colon by gut bacteria. Dietary fibre synonyms dietary fibre pronunciation dietary fibre translation english dictionary definition of dietary fibre.
Dietary fiber is a plant based nutrient that is sometimes called roughage or bulk. The functions of dietary fiber or roughage have been described in ancient herbs and medicinal literature around the world for hundreds of years. When dietary fibre reaches the large intestine the bacteria present release enzymes that cause the fibre to be broken down into smaller molecules such as butyric acid ch 3 ch 2 ch 2 cooh.
Dietary fiber british spelling fibre or roughage is the portion of plant derived food that cannot be completely broken down by human digestive enzymes. It has two main components. Regardless of the fibre source either naturally occurring in foods or added during food reformulation and production both forms become part of the total fibre content of the food according to iom dietary reference intake institute of medicine iom national academy of sciences 2005.
The definition of dietary fibre. Jones in encyclopedia of grain science 2004. Methods that can be employed to improve the nutritive.
The role of grains as a source of carbohydrate energy dietary fiber protein essential fatty acids vitamin b and minerals varies depending on the ratio of unrefined and refined grain in the diet the degree and method of milling and the actual grain used.