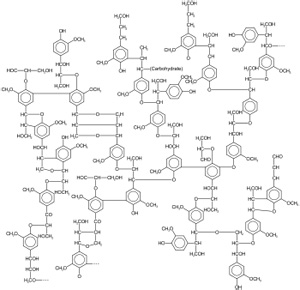
Dietary Fibre Chemical Structure

Later it was used to describe a class of plant originated polysaccharides which cannot be digested and absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract van der kamp 2004 over the past five decades confusion existed in defining df and in.
Dietary fibre chemical structure. Dietary fiber british spelling fibre or roughage is the portion of plant derived food that cannot be completely broken down by human digestive enzymes. Introduction definitions and classification. Soluble fiber which dissolves in water is generally fermented in the colon into gases and physiologically active by products such as short chain fatty acids produced in the colon by gut bacteria.
Chemistry structure and properties the result is a collection of ten outstanding articles. The term dietary fibre df was first introduced in 1950s referring to plant cell wall materials. Understanding of the structure and chemical physical properties of dietary fiber is very important to the application new product development novel material exploration and so on.
Dietary fibre is plant material that cannot be digested by the body. It contains a mixture of chemically complex polysaccharides. Structural aspects of dietary fibre dietary fibre is a complex mixture of chemical entities and its concentration and composition in different sources are neither constant nor uniform 4.
Lignin is a highly cross linked complex polymer of phenylpropane units. This special issue focuses on the chemistry structure and functional and bioactive properties of dietary fiber. This physical and chemical diversity explains the number and complexity of the physiological roles attributed to dietary fibre.
Dietary fibre helps the digestive system to move the food we eat through the intestines and push the waste material out of the. Large intestine digestion of dietary fibre. Dietary fiber is a ubiquitous component of plant foods including materials of diverse chemical and morphological structure.
When dietary fibre reaches the large intestine the bacteria present release enzymes that cause the fibre to be broken down into smaller molecules such as butyric acid ch 3 ch 2 ch 2 cooh. The functions of dietary fiber or roughage have been described in ancient herbs and medicinal literature around the world for hundreds of years. Dietary fibre includes non starch polysaccharides and lignin that are not digested or absorbed in the human small intestine.