Dietary Fiber Kidney Function Inflammation And Mortality Risk

Researchers calculated dietary.
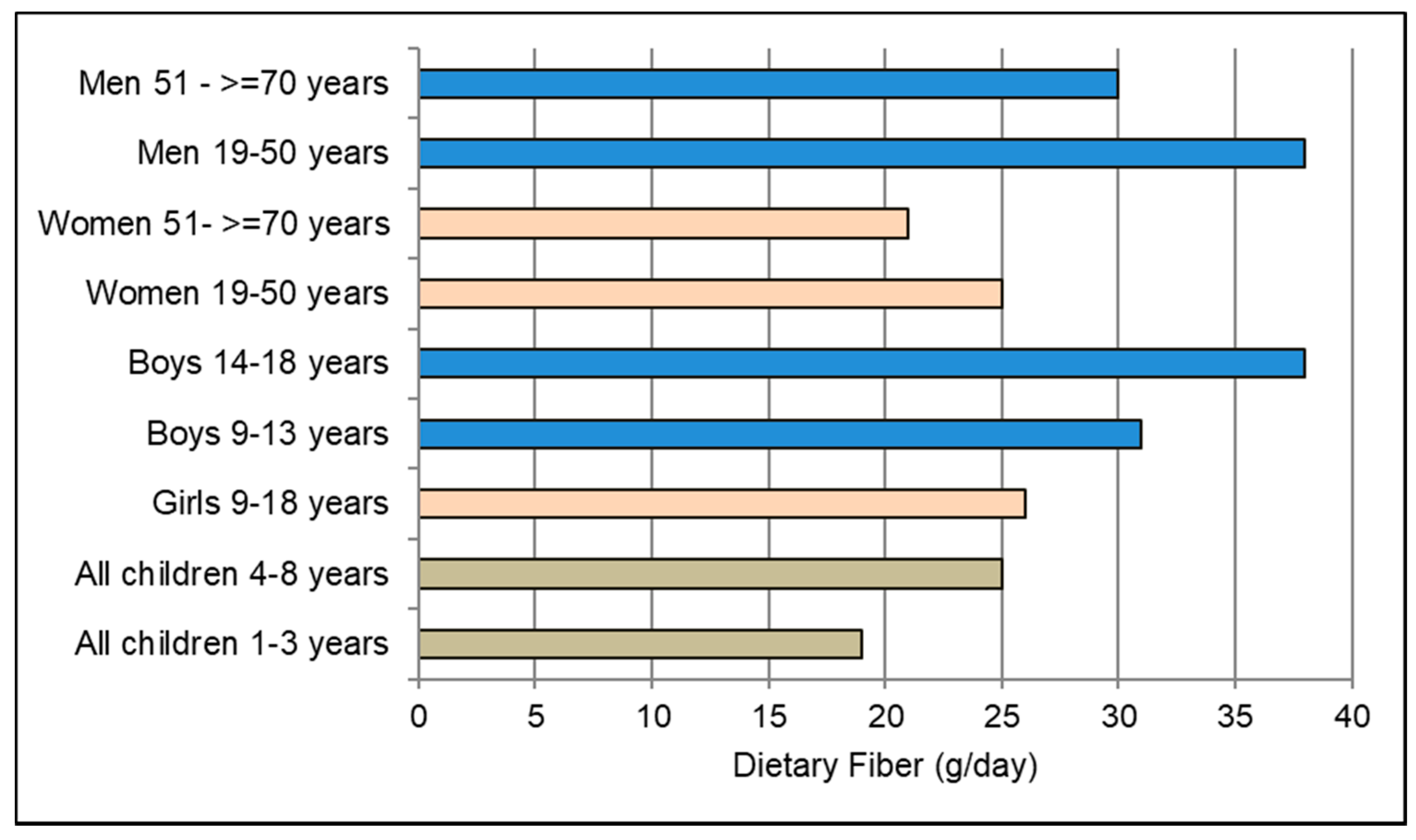
Dietary fiber kidney function inflammation and mortality risk. This study aimed to expand such findings to a northern european population. In the united states population high dietary fiber intake has been associated with a lower risk of inflammation and mortality in individuals with kidney dysfunction. Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal side effects when trying to increase their fiber intake this may be seen in irritable bowel syndrome and dyspepsia.
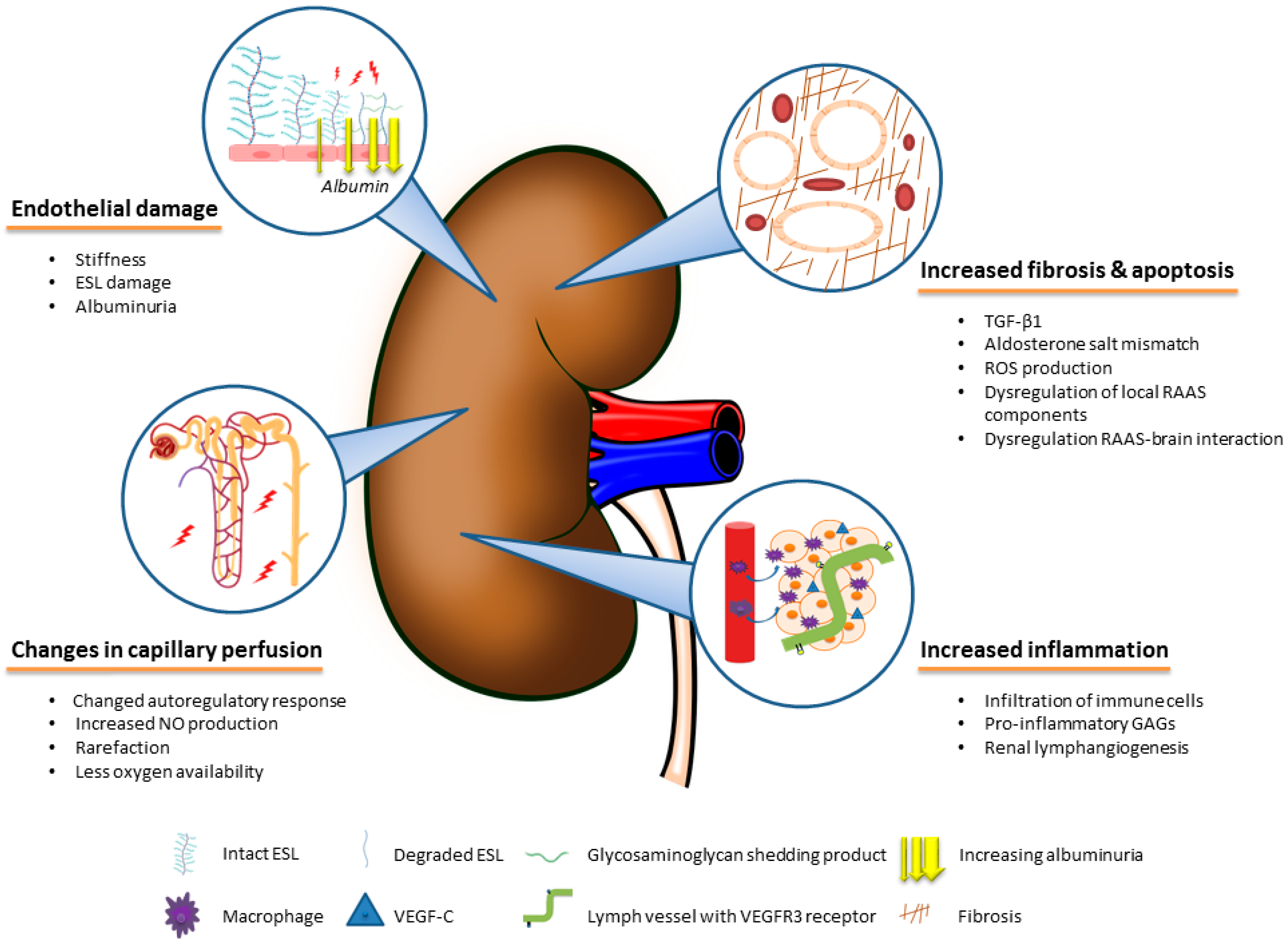
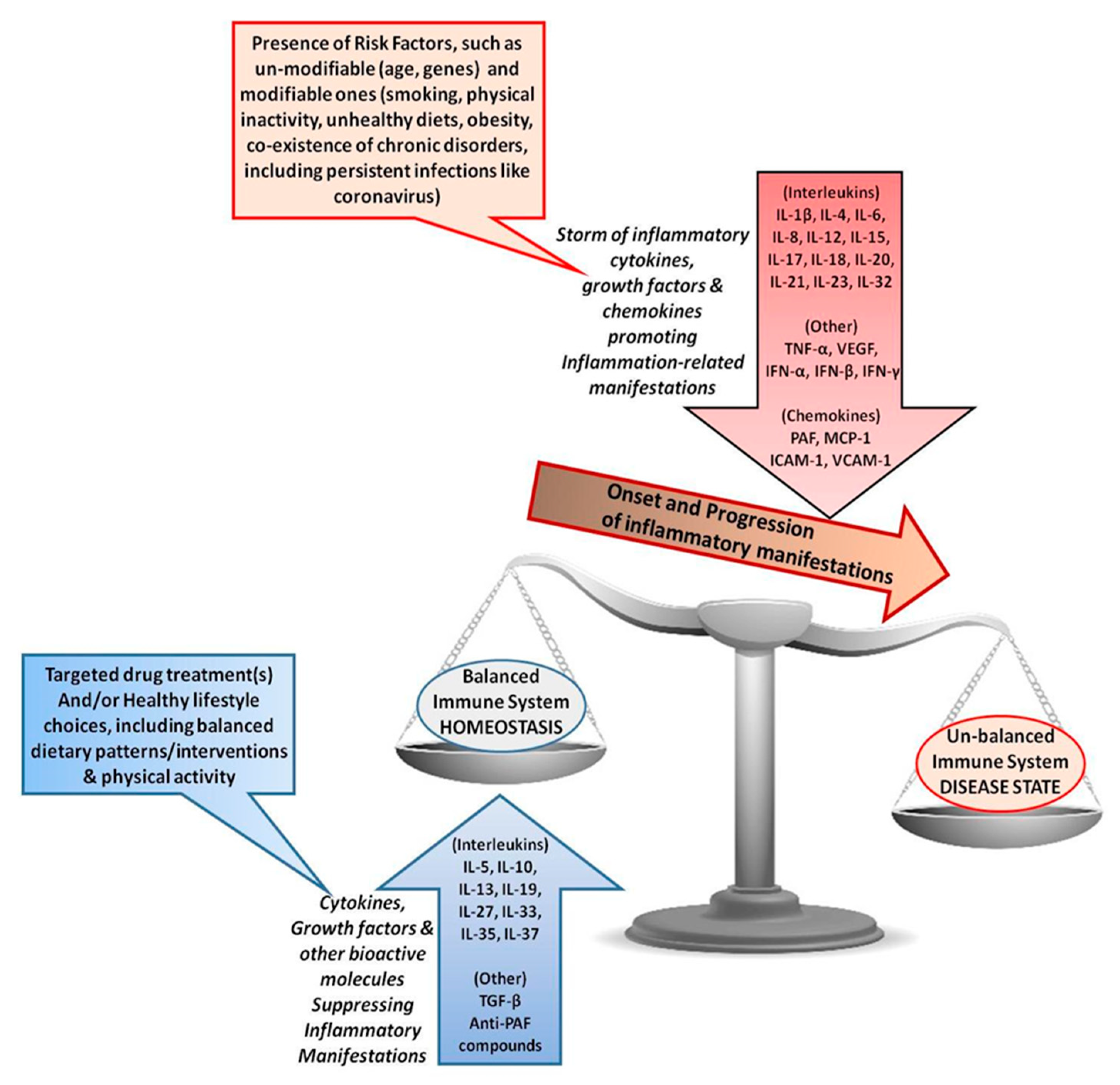
Although substantial improvements have been made in clinical care ckd remains a major public health burden affecting 10 15 of the population and its prevalence is constantly growing. Chronic diseases and inflammation the immune and metabolic systems are closely related and act in an interdependent fashion. Dietary fiber kidney function inflammation and mortality risk.
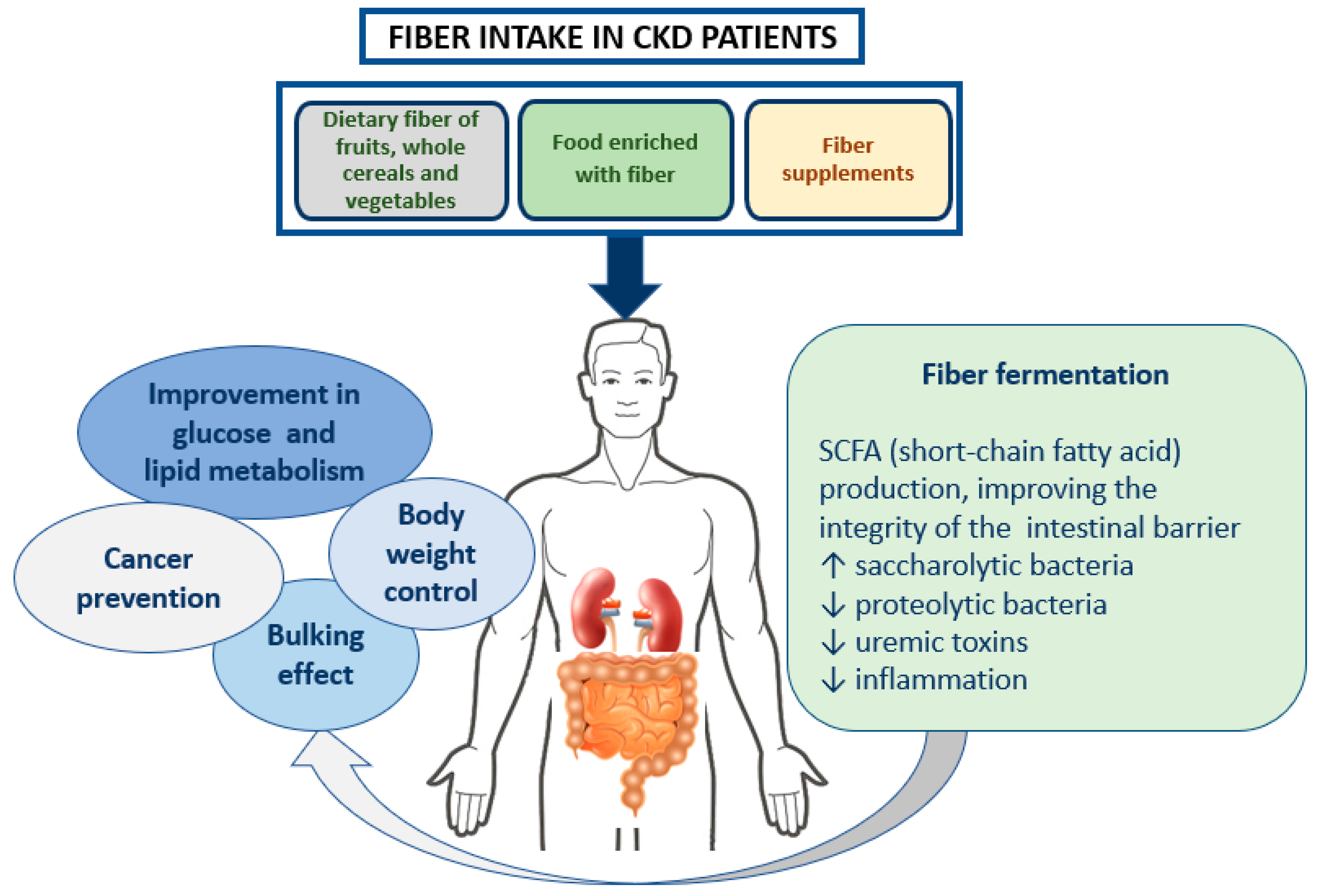
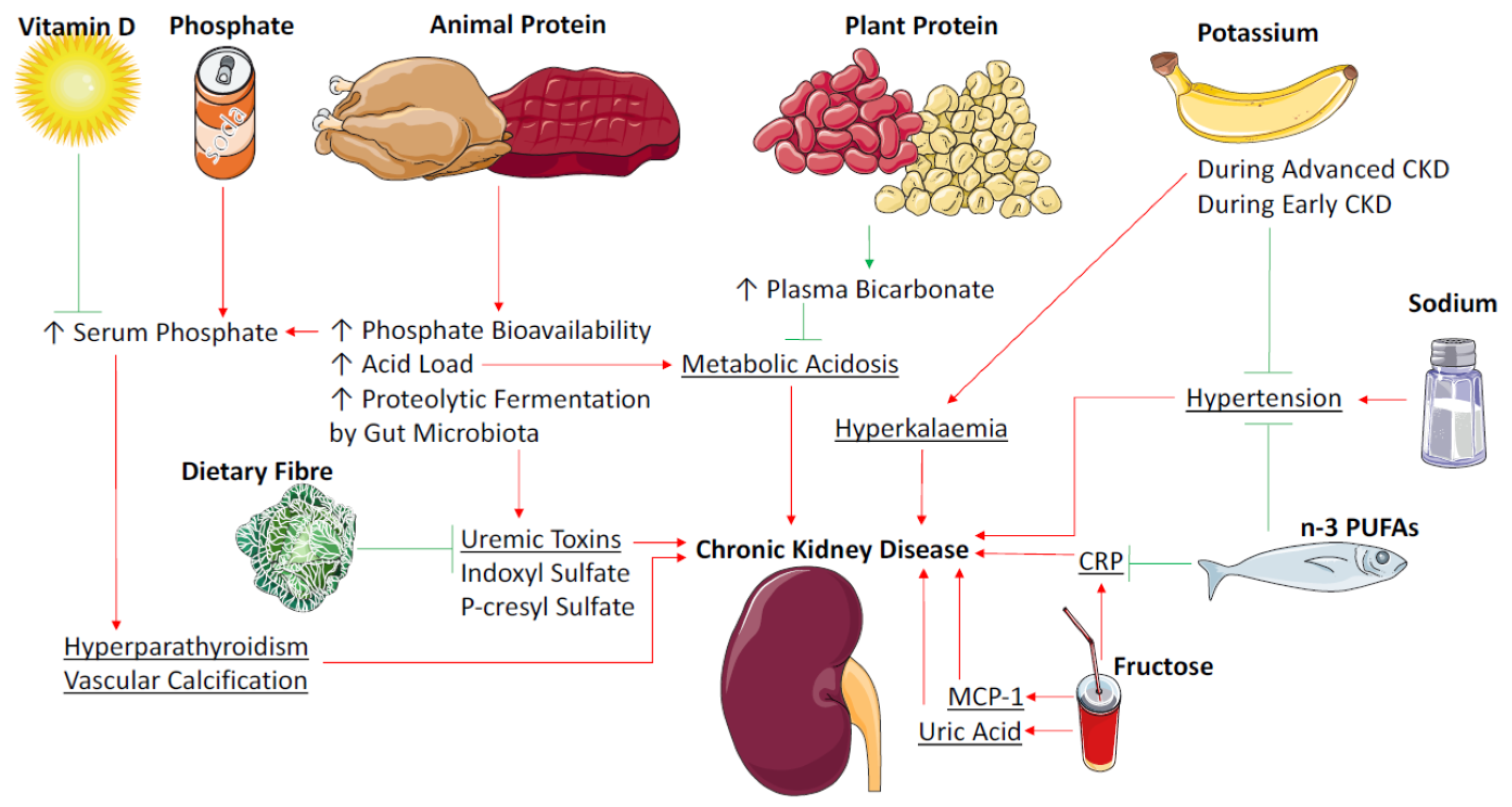
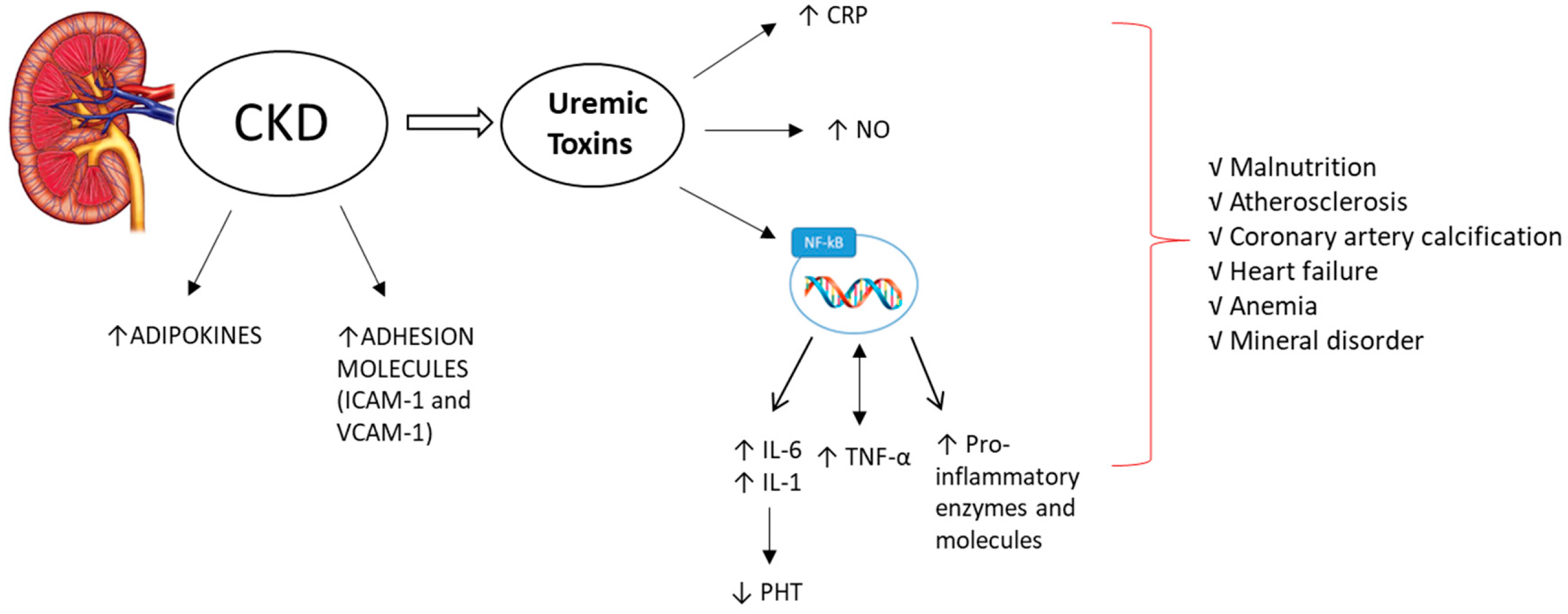
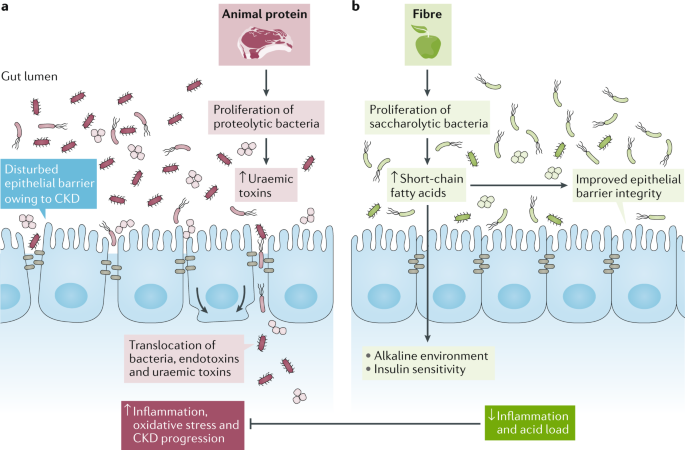
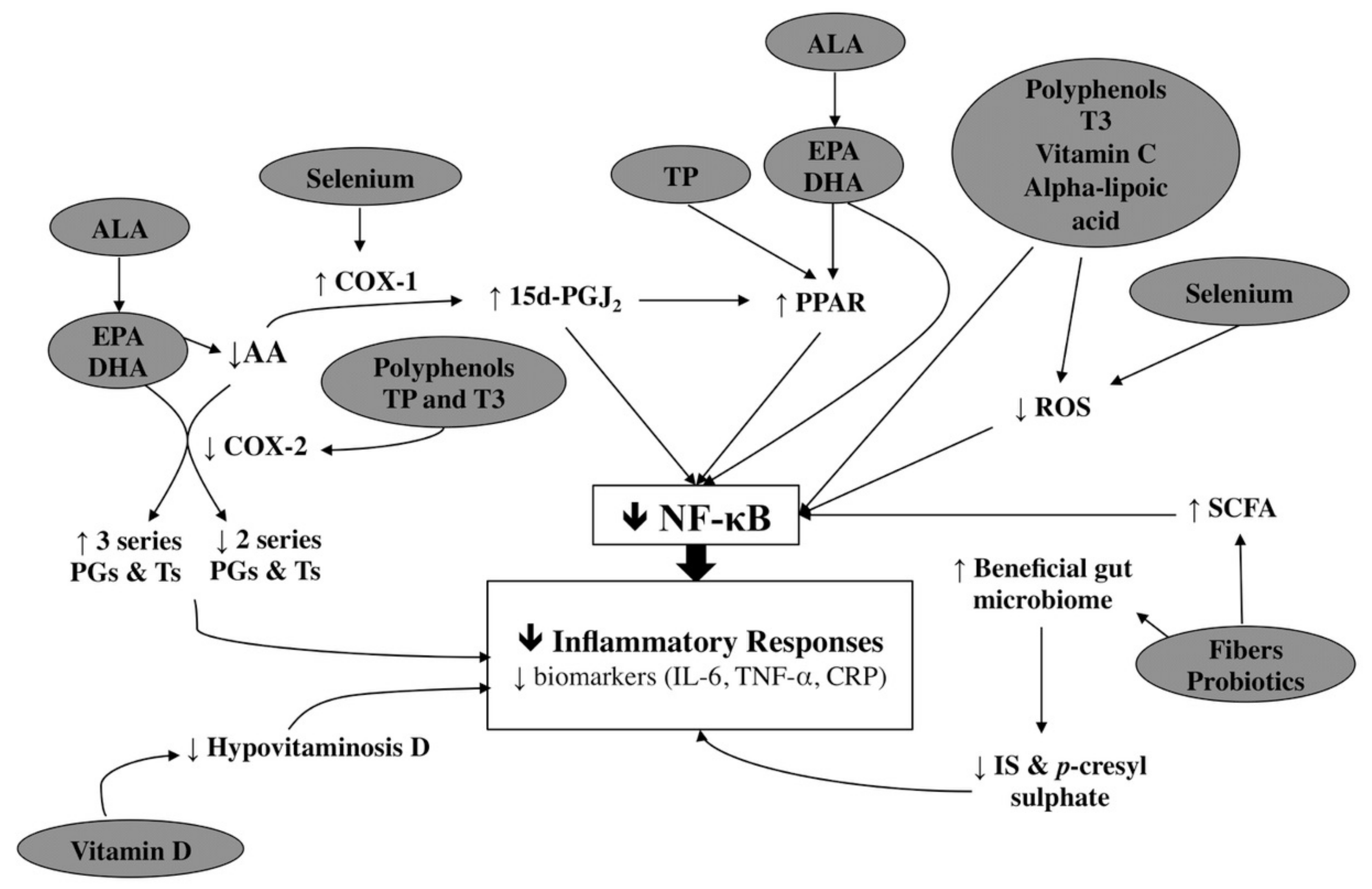
The consumption of dietary fiber df 8 can positively affect gut health as well as non gastrointestinally related conditions such as diabetes cardiovascular disease nonalcoholic fatty liver disease nafld and chronic kidney disease ckd df has a variety of physiologic effects 6 8 such as fostering the growth of select gut microbes altering the. Persistent low grade inflammation is now considered a hallmark feature of chronic kidney disease ckd being involved in the development of all cause mortality of these patients. Effects of dietary fiber intake on inflammation in chronic diseases 255 thus this paper presents the association between dietary fibers and inflammatory process markers im and their possible mechanism of action.
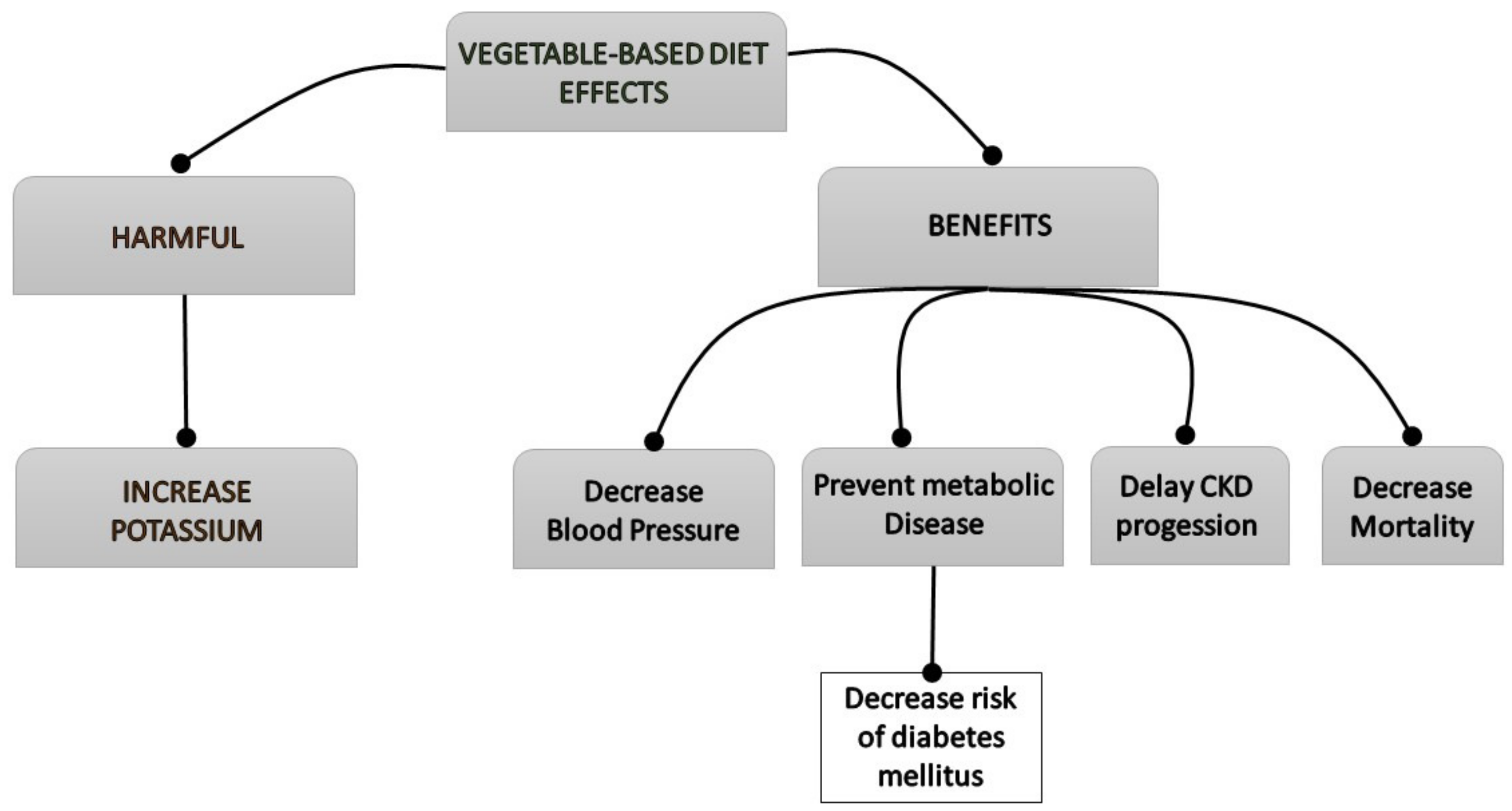
Considering the association of fiber and hard outcomes high dietary total fiber intake has been linked with better kidney function and a lower risk of inflammation and mortality in ckd patients of north america and northern europe. Design setting participants measurements. Another recent study published in the journal of renal nutrition in may 2013 conclude that increasing fiber intake in ckd patients through the consumption of foods with added fiber supplemental fiber can reduce serum creatinine levels.
Higher dietary fiber intake is linked to better kidney function and lower risk of inflammation and mortality. In the united states population high dietary fiber intake has been associated with a lower risk of inflammation and mortality in individuals with kidney dysfunction. Clin j am soc nephrol 2014.
Cas article google scholar. Dietary fiber also has the ability to reduce inflammation and all cause mortality in chronic kidney disease.