Pharmacokinetics Of The Dietary Supplement Creatine

Pharmacokinetics of the dietary supplement creatine.
Pharmacokinetics of the dietary supplement creatine. We examined the plasma concentration curve obtained over 6 h after the ingestion of 2 g of creatine cr equivalent to 2 3 g cr x h2o contained in meat or in solution in five non users of creatine supplements. Muscle creatine uptake and creatine transporter expression in response to creatine supplementation and depletion. In the 1990s athletes started to catch on and creatine became a popular.
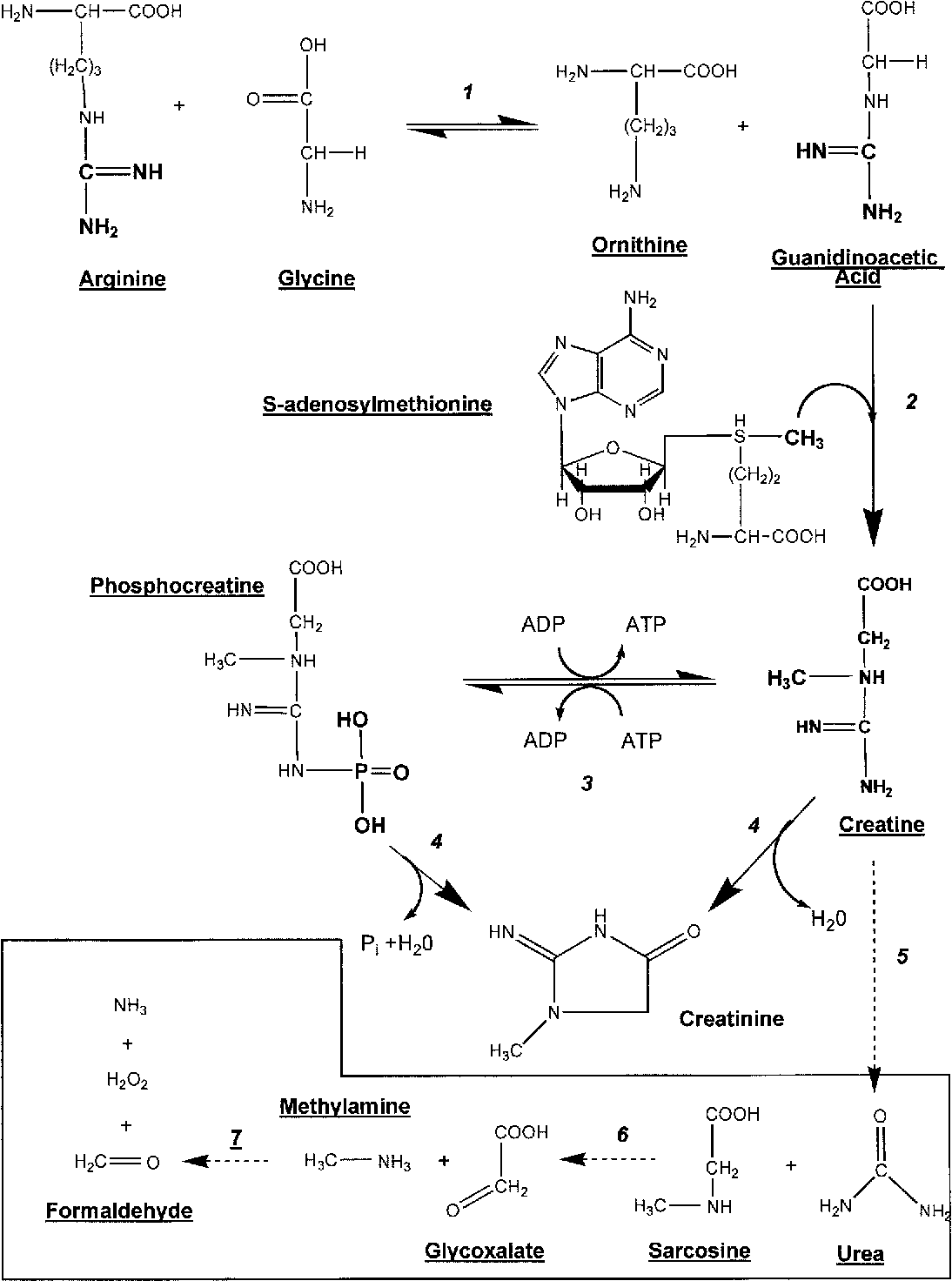
Recent research on creatine has demonstrated positive therapeutic results in various clinical applications. Studies have demonstrated that dietary supplementation with creatine can increase total skeletal muscle creatine levels by approximately 20. Of the increased deposition of creatine in the muscle after dietary supplementation approximately one third is in the form of creatine phosphate and is available for immediate use 5 6 7.
Creatine is a dietary supplement purported to improve exercise performance and increase fat free mass. Peak plasma creatine concentration was lower after the ingestion of meat but was maintai. This species exists in various modifications in solution creatine is found in vertebrates where it facilitates recycling of adenosine triphosphate atp the energy currency of the cell primarily in muscle and brain tissue.
The purpose of this review is to focus on the clinical pharmacology and therapeutic application of creatine supplementation. The body s liver pancreas and kidneys also make creatine. Though it can be made synthetically most people get creatine through seafood and red meat.
Recycling is achieved by. The clinical relevance of creatine supplementation is based p. Creatine ˈ k r iː ə t iː n or ˈ k r iː ə t ɪ n is an organic compound with the nominal formula h 2 n hn cn ch 3 ch 2 co 2 h.
Creatine is an amino acid located mostly in your body s muscles as well as in the brain. Your body converts creatine to phosphocreatine and stores it in your muscles where it s used for energy. To determine if ingestion of the dietary supplement creatine ethyl ester results in statistically and clinically relevant elevation in serum and urine creatinine levels a crossover trial in which participants will receive creatine ethyl ester or creatine monohydrate will be employed.